
Menu






Environmental factors, poor diet, and stress are common causes of inflammation. Recognizing the symptoms such as redness, swelling, and pain is crucial.
The good news is that diet plays a significant role in reducing inflammation. This article will explore the top anti-inflammatory foods to add to your diet for better health and well-being.
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection characterized by redness, swelling, heat, and pain. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, is a prolonged immune response that can lead to various chronic diseases affecting the immune system.
When an injury or pathogen enters the body, the immune system triggers an inflammatory response as a protective mechanism to remove harmful stimuli and initiate the healing process. Acute inflammation is usually short-lived and essential for tissue repair, while chronic inflammation persists for an extended period and can damage healthy tissues over time. This constant activation of the immune system in chronic inflammation not only weakens the body’s defense mechanism but can also contribute to the onset and progression of serious health conditions.
Inflammation can be caused by various factors including environmental exposures, poor diet choices, and stress levels. Chronic inflammation is often associated with autoimmune diseases where the immune system attacks healthy cells and tissues.
Environmental triggers such as pollution, toxins, and allergens can stimulate the body’s inflammatory response, leading to a cascade of reactions. Additionally, dietary habits play a crucial role in inflammation, with excessive consumption of processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats contributing to systemic inflammation. High levels of stress can also trigger inflammation by releasing stress hormones that disrupt the body’s immune balance. Understanding these diverse causes of inflammation is essential in managing and preventing chronic health conditions.”
Environmental factors such as pollution, toxins, and allergens can contribute to a chronic inflammatory state in the body, exacerbating conditions like asthma and allergies.
These external factors can trigger an immune response, causing the body to release inflammatory chemicals that are meant to protect against perceived threats. Prolonged exposure to pollutants and allergens can lead to a persistent state of inflammation, which can be detrimental to overall health. When the body remains in this heightened inflammatory state, it can worsen pre-existing health conditions, making them more difficult to manage and control. In the long run, chronic inflammation can contribute to the development of serious illnesses such as cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune disorders, and even certain types of cancer.
A poor diet rich in processed foods, sugary beverages, and trans fats can increase the risk of chronic diseases by promoting inflammation.
Research has shown that diets high in processed foods and added sugars can trigger inflammation in the body, which is linked to conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. These inflammatory responses can lead to a cascade of harmful effects on overall health.
On the other hand, anti-inflammatory diets, such as the Mediterranean and DASH diets, emphasize whole, nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These diets are rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and other nutrients that help combat inflammation and promote overall well-being.
Chronic stress can contribute to the dysregulation of the immune system, leading to chronic inflammation and an increased risk of autoimmune diseases.
When the body experiences chronic stress, the release of stress hormones such as cortisol can disrupt the balance of the immune system, triggering a cascade of inflammatory responses. This persistent inflammation can have detrimental effects on various organs and tissues, increasing susceptibility to conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and even certain types of cancer.
Managing stress is crucial in preventing these harmful effects on the body. Implementing relaxation techniques, such as mindfulness meditation or yoga, can help reduce stress levels and promote overall well-being.
The symptoms of inflammation can manifest as redness, swelling, pain, and discomfort at the site of injury or infection. Immune helper cells play a crucial role in the inflammatory response by releasing cytokines to recruit other immune cells.
Inflammation is the body’s natural defense mechanism, indicating that the immune system is actively working to heal and protect from harm. When tissue becomes damaged or infected, the immune system springs into action. Redness (erythema), often due to increased blood flow, is a visible sign of the body mobilizing resources to the affected area. Swelling (edema), caused by fluid accumulation, helps isolate the injury and prevent further damage.
Pain is a warning signal that alerts an individual to the presence of inflammation. It occurs due to the release of various signals that sensitize nerves in the affected area. These signals, including cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), trigger responses that promote healing. Immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, are recruited to the site, where they release more cytokines.
Redness and swelling are classic signs of inflammation caused by the release of inflammatory markers such as NF-κB in response to tissue damage or infection.
When there is tissue damage or an infection, the immune system triggers a cascade of events to protect the body. One vital player in this process is the transcription factor NF-κB, which acts as a key regulator of inflammation. NF-κB activates genes that produce inflammatory molecules, leading to the dilation of blood vessels and increased permeability. As a result, the affected area becomes red and swollen, allowing immune cells to reach the site more easily. These visible signs are essential indicators that the body’s defenses are actively working to combat the threat.
Pain and discomfort are common symptoms of inflammation that can be alleviated by anti-inflammatory compounds such as polyphenols found in various fruits, vegetables, and herbs.
When inflammation occurs in the body, it triggers a cascade of responses that can lead to discomfort and pain, affecting daily life and overall well-being. In such situations, the consumption of foods rich in polyphenols can play a vital role in managing these inflammatory symptoms. Polyphenols are powerful antioxidants that help combat the oxidative stress associated with inflammation, thereby reducing the severity of pain and discomfort.
Difficulty moving can be a consequence of inflammation, particularly in chronic diseases where oxidative stress and free radicals affect joint mobility. Antioxidants like flavonoids can help alleviate inflammation and improve mobility.
When inflammation is present in the body, it can lead to swelling, pain, and stiffness in the joints, making it challenging to engage in regular physical activities or even perform simple daily tasks.
In chronic conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, the ongoing inflammatory response can progressively erode joint cartilage and lead to permanent damage, further limiting mobility.
Flavonoids, found in colorful fruits and vegetables, can combat oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals that contribute to inflammation. By reducing inflammation, these powerful antioxidants help in preserving joint function and supporting increased range of motion.
Diet plays a crucial role in modulating inflammation through the consumption of anti-inflammatory foods rich in dietary long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. These foods can help lower inflammatory markers and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
When incorporated into a balanced diet, dietary long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids found in sources such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts have shown promising results in reducing inflammation levels within the body. Research suggests that these foods not only combat inflammation but also promote cardiovascular health and support the immune system, thus playing a significant role in overall well-being. By actively choosing to include these anti-inflammatory foods in your daily meals, you are taking proactive steps towards improving your health and potentially preventing the onset of various inflammatory conditions.
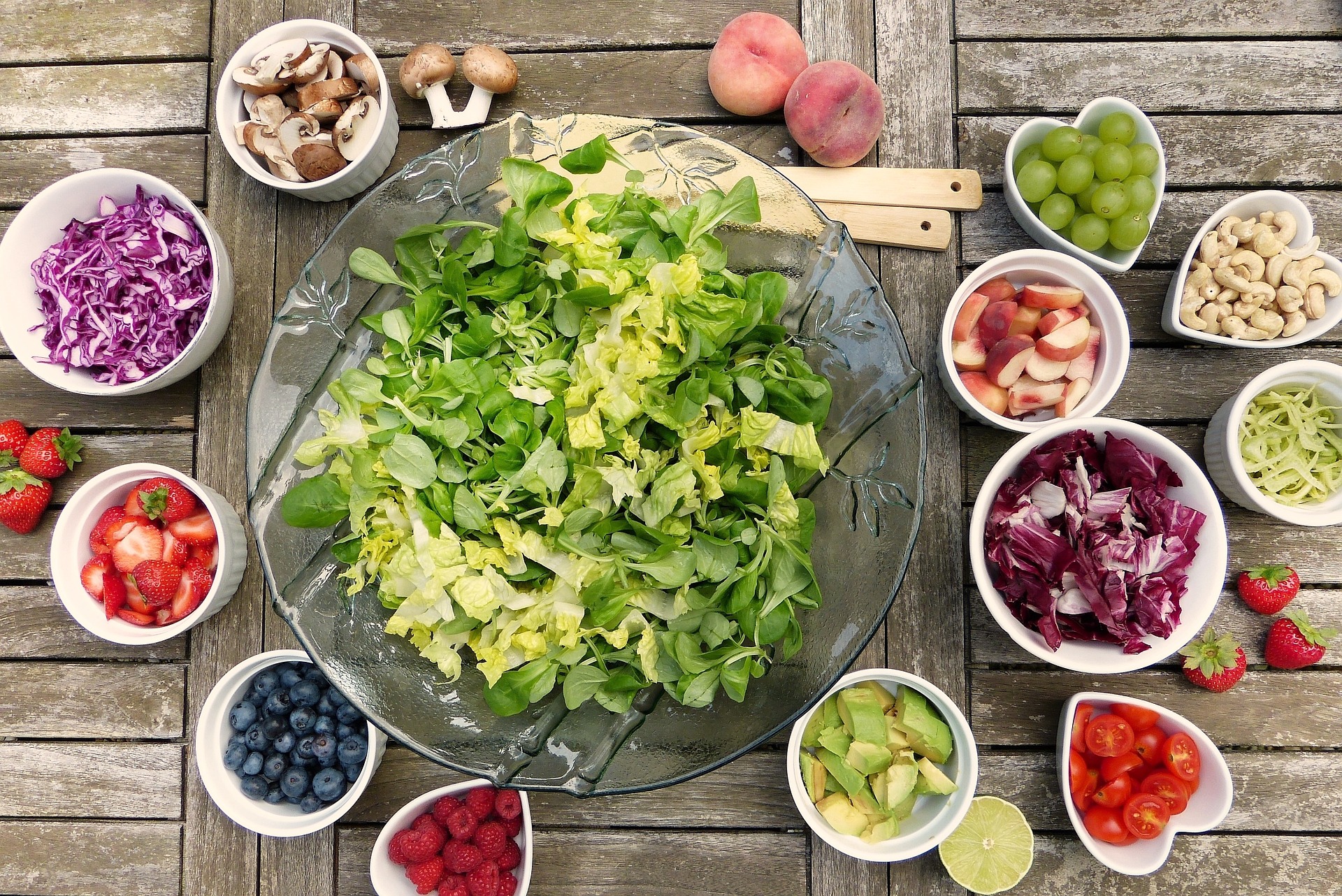
Including top anti-inflammatory foods in your diet, such as fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, dark leafy greens loaded with antioxidants, and vibrant fruits can significantly aid in fighting inflammation and enhancing your well-being.
These foods offer a multitude of benefits beyond their anti-inflammatory properties. For example, omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish have been linked to reduced risk of heart disease and improved brain function.
The antioxidants present in dark leafy greens help protect cells from damage and boost the immune system, while colorful fruits provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber that support overall health.
By incorporating a variety of these nutrient-dense foods into your meals, you can create a balanced diet that not only fights inflammation but also nourishes your body from within.
Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, essential for combating chronic inflammation and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in the body’s inflammatory response, helping to regulate the immune system and decrease inflammation levels.
By incorporating fatty fish into your diet regularly, you can potentially lower the risk of conditions such as heart disease, arthritis, and even certain types of cancer.
These beneficial fats not only support heart health but also aid in maintaining cognitive function and promoting healthy skin.
The consumption of omega-3 rich fish can improve overall well-being, offering a tasty and nutritious way to boost your health naturally.
Leafy greens like spinach and kale are packed with antioxidants that can help reduce inflammation and support the immune system. They are staples of the Mediterranean diet known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Incorporating a variety of leafy greens into your diet not only adds a burst of color and flavor to meals but also provides a plethora of health benefits. The antioxidants found in spinach and kale combat oxidative stress in the body, which is linked to inflammation and various chronic diseases. By following the principles of the Mediterranean diet and including these greens in your daily meals, you can enhance your body’s defense against inflammation and improve overall well-being.
Berries such as blueberries and strawberries are rich in polyphenols, powerful antioxidants that can combat chronic inflammation and oxidative stress in the body.
These polyphenols work by reducing the production of inflammatory molecules in the body, thus helping to alleviate symptoms of conditions like arthritis and heart disease.
The antioxidant properties of berries help to neutralize harmful free radicals that can lead to cell damage and aging.
By incorporating a variety of berries into your diet, you can enhance your body’s defenses against chronic inflammation and support overall health.
Nuts and seeds like walnuts and chia seeds are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids and other anti-inflammatory compounds that can help lower inflammation levels in the body.
Incorporating these nutrient powerhouses into your daily diet can have a multitude of benefits beyond just reducing inflammation. The omega-3 fatty acids found in walnuts and chia seeds are known for their heart-healthy properties, helping to lower cholesterol levels and improve cardiovascular health. The anti-inflammatory properties of these foods can support joint health, reducing stiffness and discomfort associated with conditions like arthritis.
The rich vitamin and mineral content of nuts and seeds, such as vitamin E, magnesium, and zinc, can bolster the immune system and promote overall well-being. By including a variety of nuts and seeds in your meals, you can create a diverse and flavorful array of dishes while reaping the numerous health benefits they offer.
Turmeric, a spice containing curcumin, has been used for its anti-inflammatory properties and potential in reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
The therapeutic effects of turmeric and curcumin in combating inflammation have been widely studied and celebrated. Research suggests that these potent herbs can help alleviate symptoms associated with conditions like arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and other inflammatory disorders.
Regular consumption of turmeric may also aid in reducing oxidative stress and improving overall immune function. The traditional use of turmeric in promoting health and well-being dates back centuries in various cultures, highlighting its versatile benefits beyond just its taste-enhancing properties.
Ginger, known for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, can help reduce inflammatory markers and support overall health as part of an anti-inflammatory diet.
Ginger has been shown to have a positive effect on gut health by aiding digestion and alleviating gastrointestinal distress. This versatile spice can be added to various dishes, teas, and smoothies to not only enhance flavor but also boost nutritional value. Studies suggest that the bioactive compounds in ginger, such as gingerol, have potent anti-inflammatory effects that may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Olive oil, rich in monounsaturated fats, is a key component of the Mediterranean diet known for its protective effects on the immune system and ability to reduce chronic inflammation.
Due to its high content of monounsaturated fats, olive oil is revered for its anti-inflammatory properties, which can help in reducing the risks of various chronic diseases. The monounsaturated fats in olive oil contribute to lowering inflammation levels in the body, thus promoting overall well-being and immune system health. By integrating olive oil into your daily meals, you are not only enhancing the taste of your dishes but also supporting your body’s natural defense mechanisms against inflammation.
Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice are excellent sources of dietary fiber and nutrients that can help reduce the risk of chronic diseases by supporting the immune system.
In terms of an anti-inflammatory diet, the role of whole grains cannot be overstated. The abundance of dietary fiber found in grains like quinoa and brown rice plays a crucial part in maintaining gut health and reducing inflammation throughout the body.
Not only do these fiber-rich grains aid in digestion and promote a healthy microbiome, but they also help regulate blood sugar levels and support heart health. By incorporating whole grains into your daily meals, you are not only nourishing your body with essential nutrients but also actively working towards preventing various chronic conditions.
Garlic, rich in sulfides, is recognized for its anti-inflammatory properties that can enhance immune helper cells’ function and support the body’s defense mechanisms.
Studies suggest that the sulfides in garlic play a vital role in reducing inflammation by inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory compounds. By modulating the activity of immune cells, garlic helps in regulating the immune response, making it more efficient in fighting off infections and diseases. Additionally, allicin, a key component in garlic, has been found to have potent antimicrobial properties, further boosting the body’s ability to ward off pathogens. This potent combination of anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting effects makes garlic a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Avocado, rich in antioxidants and healthy fats, is a versatile fruit that can help combat chronic inflammation and support overall health as part of an anti-inflammatory diet.
Avocados are a nutritional powerhouse due to their high content of antioxidants such as Vitamin E, Vitamin C, and various carotenoids. These antioxidants play a crucial role in fighting oxidative stress and reducing inflammation in the body. Avocados are a great source of monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, which is known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
By incorporating avocados into your meals, you not only enhance the flavors but also boost your intake of essential nutrients that can help lower the risk of chronic diseases linked to inflammation, such as heart disease and arthritis. Including avocados in a well-balanced diet can contribute to overall wellness and long-term health benefits.
The top anti-inflammatory foods to add to your diet include leafy green vegetables, fatty fish, berries, nuts and seeds, turmeric, and olive oil.
These foods contain high levels of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds that help reduce inflammation in the body.
Consuming anti-inflammatory foods can improve overall health by reducing chronic inflammation, which has been linked to various health issues such as heart disease, arthritis, and certain types of cancer.
Yes, you can still enjoy other foods in moderation while incorporating these anti-inflammatory foods into your diet. These foods are meant to be added to a well-balanced and varied diet.
Some of these foods, such as turmeric and olive oil, are best consumed when cooked with heat to release their anti-inflammatory properties. However, consuming them raw or in their natural state also provides benefits.
Yes, these foods can be beneficial for everyone as part of a healthy diet. They can help prevent chronic inflammation and promote overall wellness, regardless of any existing health conditions.
Discover insights and guidance on detoxification, nutrition, and overall wellness. Elevate your health journey with our expertly curated articles and empower yourself to make informed decisions for a healthier lifestyle.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.



Subscribe to our newsletter and we’ll send you the emails of latest posts.
Copyright © 2024 Detox Diet. All rights reserved.